Blogs
Typical Corrosion Types

Research Your Destination
Types of Corrosion
Uniform Corrosion
Description: Evenly distributed metal loss
Causes: Corrosive environment
Typical Features: Thinning of the entire surface, often predictable
Pitting Corrosion
Description: Localized corrosion forming small pits
Causes: Aggressive ions, localized breakdown of protective film
Typical Features: Small, deep pits or cavities, rapid failure with minimal overall metal loss
Crevice Corrosion
Description: Corrosion in narrow gaps or crevices
Causes: Stagnant conditions, oxygen concentration differences, build-up of aggressive ions
Typical Features: Localized corrosion in gaps, often hidden from view
Galvanic Corrosion
Description: Accelerated corrosion due to contact with a more noble metal
Causes: The electrochemical potential difference, conductive path, presence of an electrolyte
Typical Features: Corrosion of the less noble metal, protection of the more noble metal
Intergranular Corrosion
Description: Corrosion along grain boundaries
Causes: Depletion of protective elements, sensitization during heat treatment or welding
Typical Features: Corrosion along grain boundaries may cause loss of mechanical properties
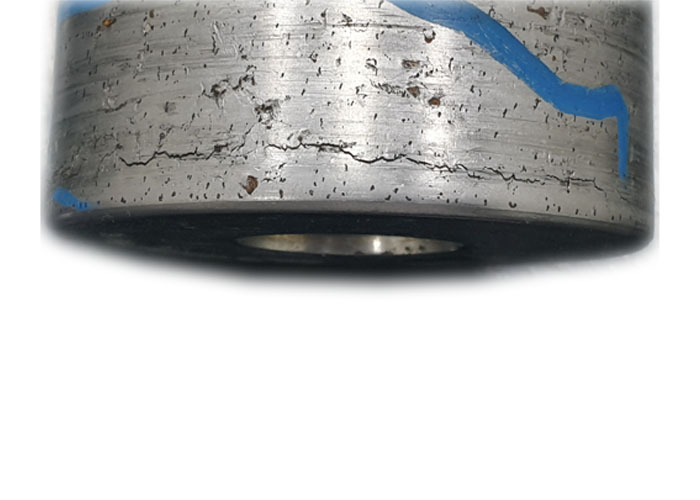
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC)
Description: Cracking due to the combined action of tensile stress and a corrosive environment
Causes: Tensile stress, susceptible material, aggressive environment
Typical Features: Brittle cracks, often originating from existing flaws, can lead to catastrophic failure
Erosion Corrosion
Description: Accelerated corrosion due to fluid flow
Causes: High fluid velocities, abrasive particles, turbulence, cavitation
Typical Features: Increased metal loss at high-flow areas, grooves, pits, or waves in the material
Microbial Corrosion
Description: Corrosion caused by microorganisms
Causes: Microorganisms, sulfate-reducing or acid-producing bacteria, presence of biofilms
Typical Features: Localized or general corrosion, accelerated by metabolic by-products, biofilm formation